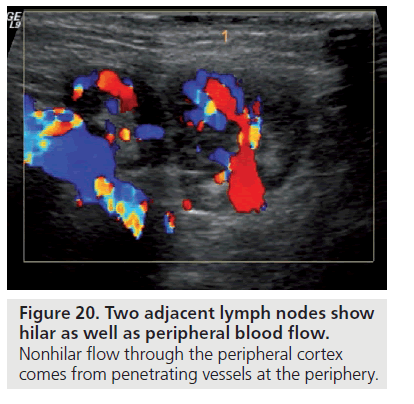
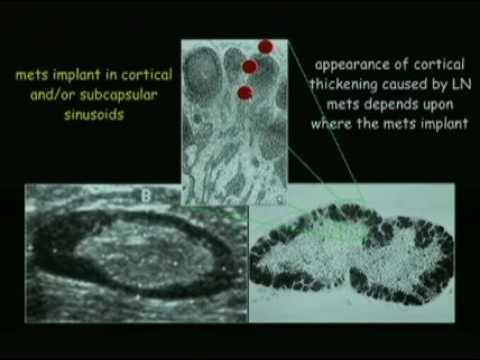
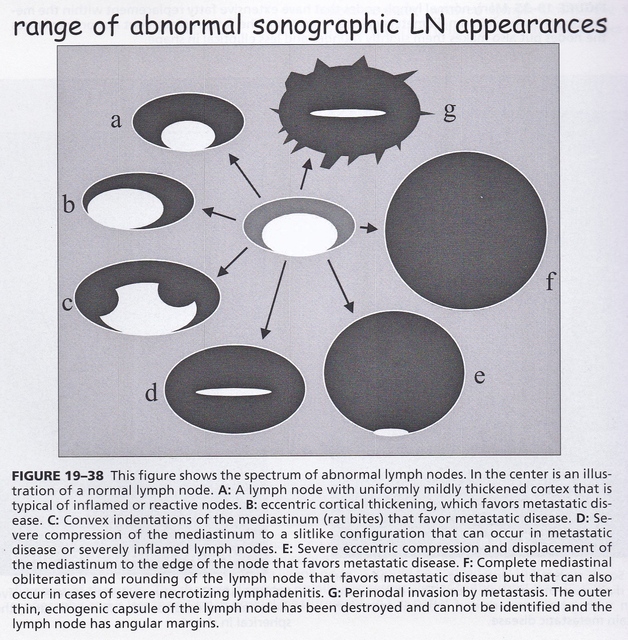
Breast Cancer Lymph Node Color Doppler Ultrasound Color Meanings
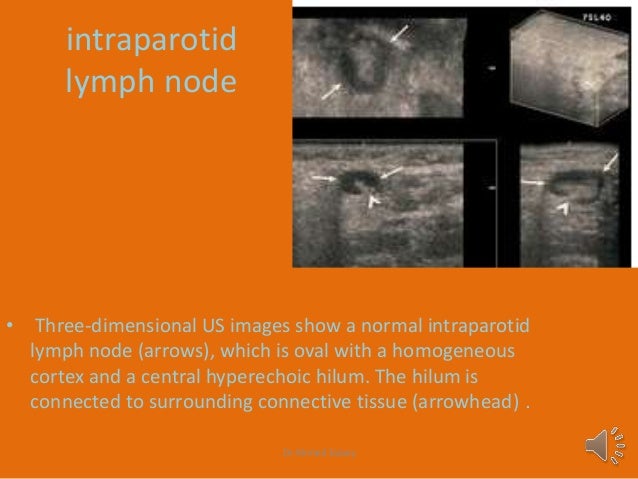
B d three dimensional multiplanar reformatted images also show loss of the fatty hilum.
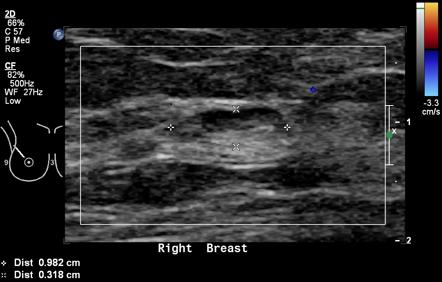
Breast cancer lymph node color doppler ultrasound color meanings. Axillary lymph node dissection alnd is the definitive method to diagnose axillary metastasis but sentinel lymph node biopsy slnb has supplanted this procedure as the primary method of evaluating the axilla in most cases of early stage breast cancer because slnb has a significantly lower rate of morbidity than does alnd and a low false. The presence of cancer cells is known as lymph node involvement. Lymph nodes are small bean shaped organs that act as filters along the lymph fluid channels. Lymphadenopathyis quite common and it can be very difficult to differentiate malignant lymphadenopathy from reactive nodal enlargement.
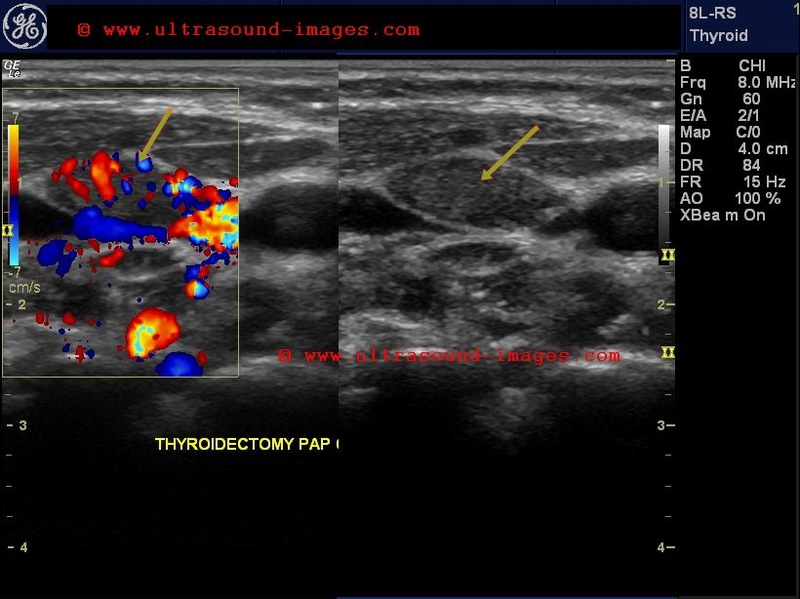
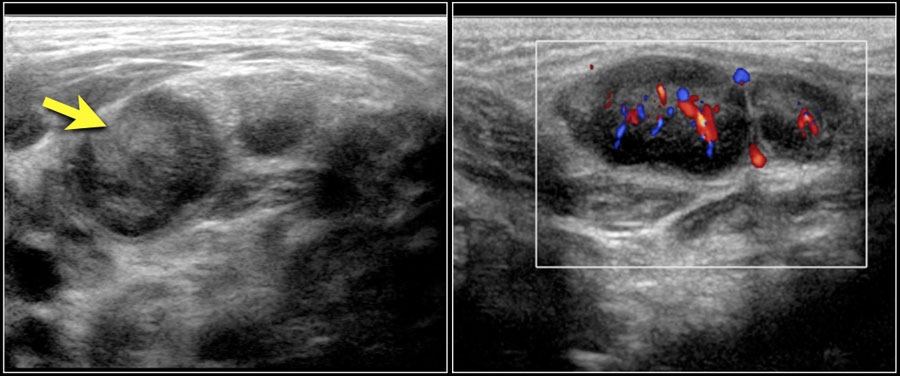
On color doppler it may show some peripheral vascularity in acute phase and may resemble breast cancer requiring a biopsy to establish tissue diagnosis. To document differences in color doppler flow and gray scale ultrasonographic us features between benign and malignant axillary lymph nodes in women with primary breast cancer. As lymph fluid leaves the breast and eventually goes back into the bloodstream the lymph nodes try to catch and trap cancer cells before they reach other parts of the body. The longitudinal transverse axis ratio and hilar status on color doppler flow and gray scale us images were prospectively studied for each of 145 axillary nodes in 135 women 74.
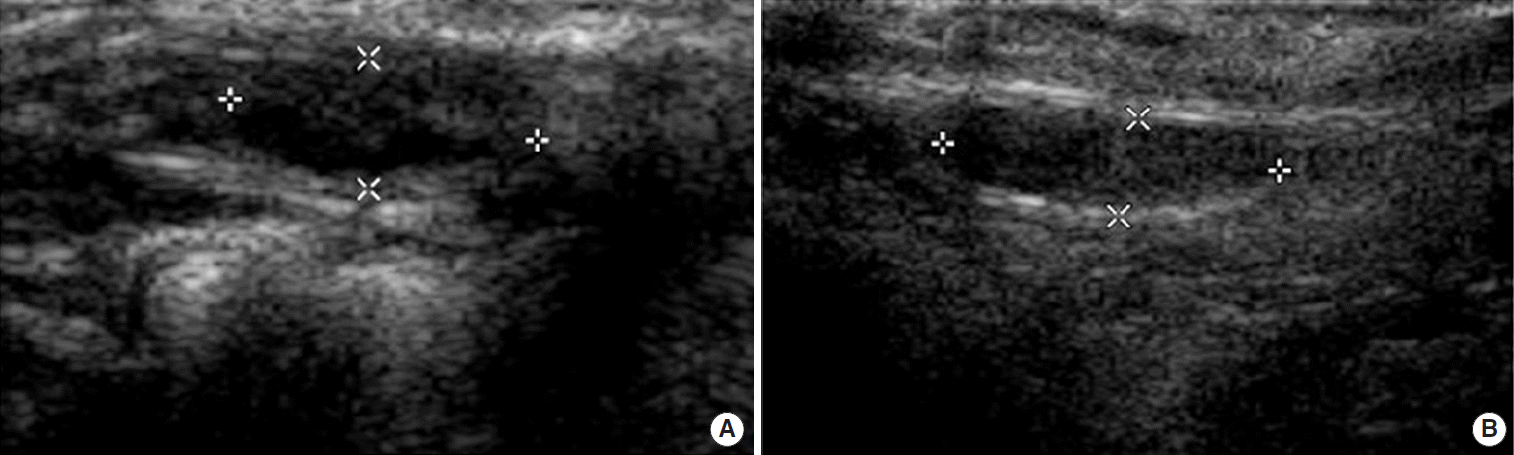
Axillary lymph node aln status is the most important prognostic factor for the management of breast cancer patients in the absence of metastatic disease. The analysis of patterns of nodal vascularity can be used to differentiate benign from malignant lymphadenopathy with high sensitivity. However fat necrosis usually exhibits no significant blood flow figure 16. Gray scale parameters that favor malignancy size.
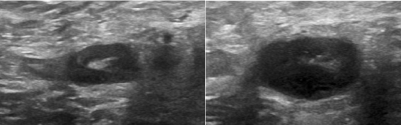
The vascular flow is inadequately evaluated. A two dimensional color doppler sonography reveals rounded lymph node morphologic characteristics with loss of hilar fat. In 1998 reports that the use of color doppler sonography on axillary lymph nodes to diagnose the metastatic axillary lymph nodes of breast cancer. However the normally directed hilar blood flow arrow which is best seen with manipulation of the images supports the histologic diagnosis of a reactive lymph node.
Color doppler ultrasound can show flow in all lymph nodes regardless of whether they are affected by a benign or a malignant process.